Explore renditions of raga Mohana, raga Bhupalam, raga Revagupti & Hindustani rag Bhupali on YouTube >>
Find song lyrics (composers) & translations for these and other ragas >>
Download this audio file (2 MB, 2 min. mono)
Credit: eSWAR / FS-3C Sruthi petti + Tanjore Tambura
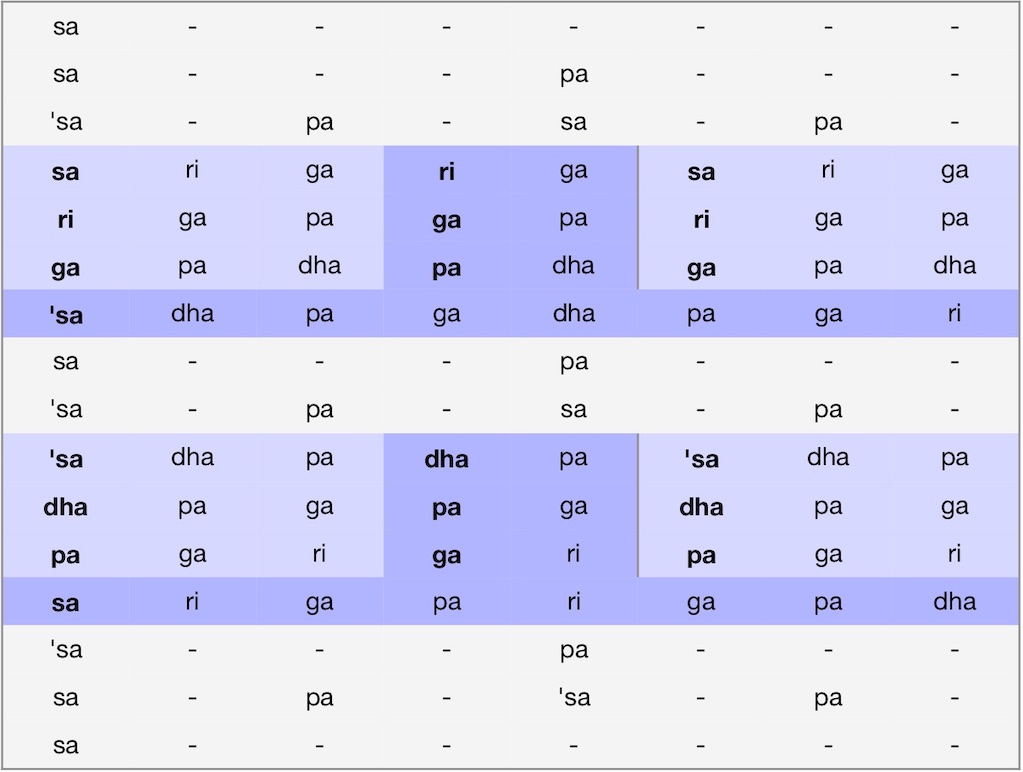
Become fluent with the help of svara syllables (solmisation): practice a series of exercises, each based on a set of melodic figures that lend themselves to frequent repetition (“getting into flow”) | Practice goal, choosing your vocal range & more tips >>
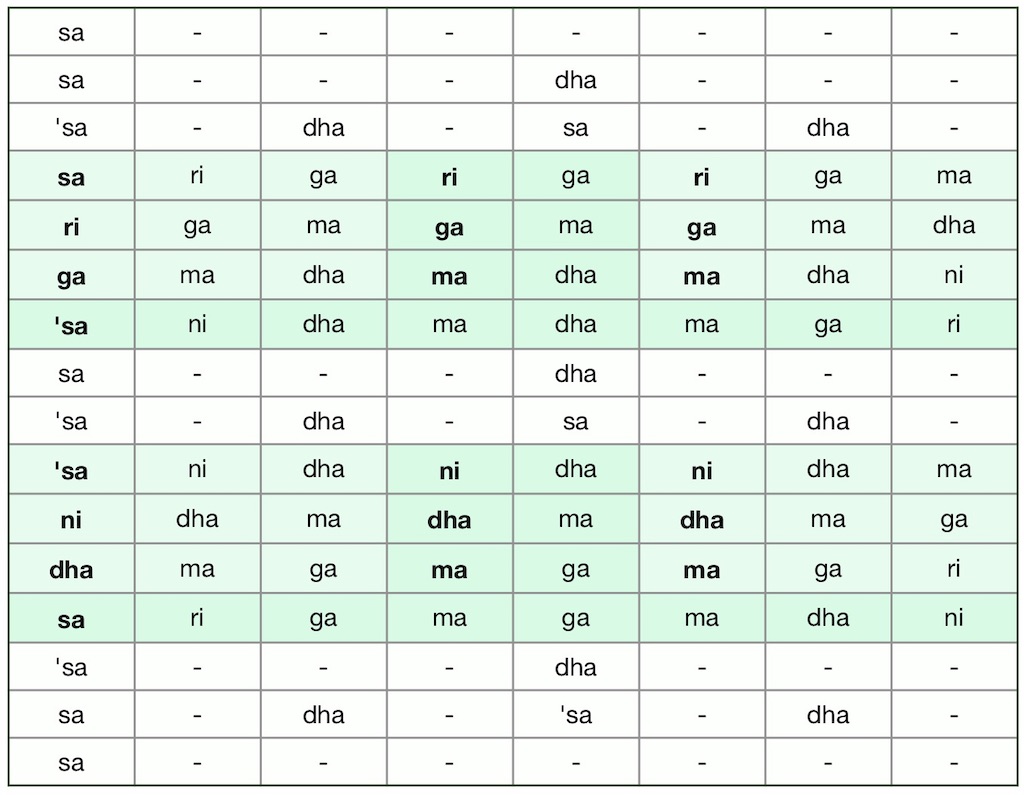
The above figures lend themselves to several ragas of Carnatic music:
South Indian conventions (raga names & svara notation): karnATik.com | Guide >>
raagam: mOhanam = raagam: bhUpALi (derived from the 28th melakarta raga, Harikambhoji)
Aa: S R2 G3 P D2 S | Av: S D2 P G3 R2 S
raagam: bhUpALam (derived from the 8th melakarta raga, Hanumatodi)1
Aa: S R1 G2 P D1 S | Av: S D1 P G2 R1 S
raagam: rEvagupti (derived from the 15th melakarta, Mayamalavagaula)2
Aa: S R1 G3 P D1 S | Av: S D1 P G3 R1 S
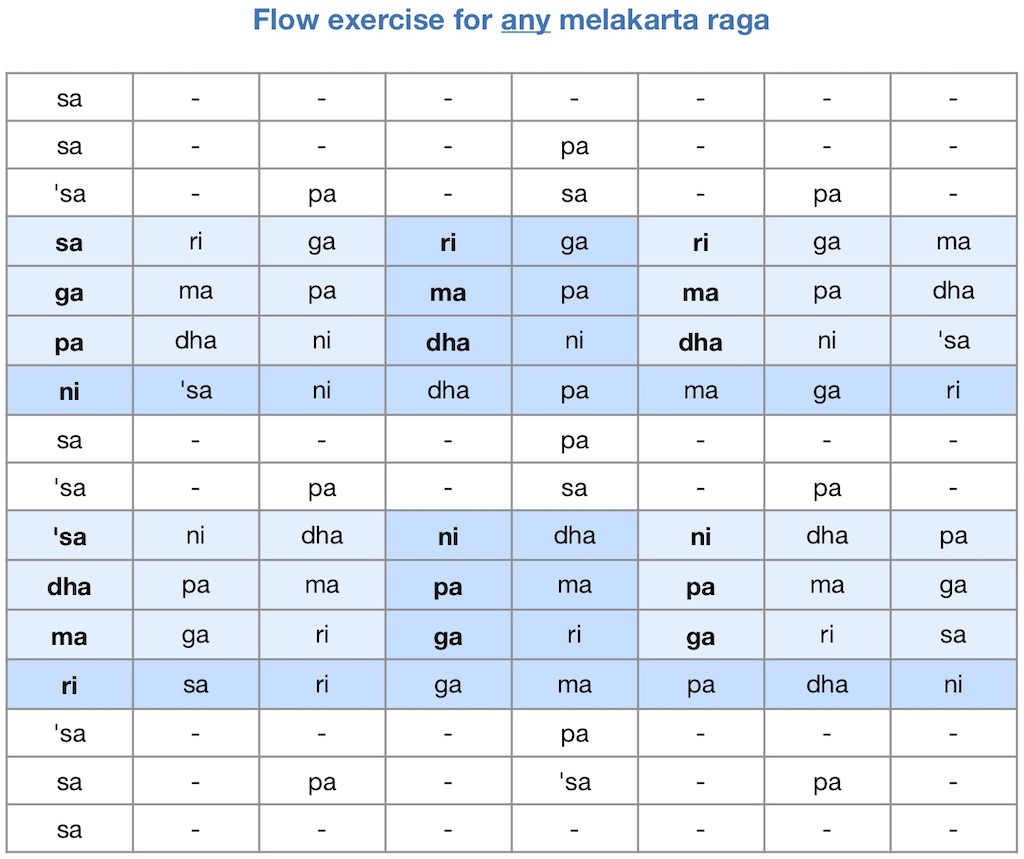
“Flow” exercises
A series of “Flow” exercises invites learners to practice all the 72 musical scales of Carnatic music (“mela” or mēlakarta rāga). It is meant to supplement the comprehensive standard syllabus (abhyāsa gānam) attributed to 16th c. composer Purandara Dasa.
Repeated practice need not be tedious; instead it instantly turns joyful whenever we remind ourselves that Indian music “is created only when life is attuned to a single tune and a single time beat. Music is born only where the strings of the heart are not out of tune.” – Mahatma Gandhi on his love for music >>
As regards “time beat” in Carnatic music, the key concept is known as kāla pramānam: the right tempo which, once chosen, remains even (until the piece is concluded). | Learn more >>
Music teachers will find it easy to create their own versions: exercises that make such practice more enjoyable. | Janta variations >>
Concept & images © Ludwig Pesch | Feel free to share in accordance with the
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license >>
Listen to Uma Ramasubramaniam demonstrating the svaras (notes) for the present raga(s) on Raga Surabhi >>
Having but 5 notes (instead of 7), this type of raga pattern is traditionally classified as being “derived” (janya) from a melakarta raga. More specifically, text books refer to any raga limited to 5 notes as audava raga.
The above svara pattern may be sung, hummed or practiced silently with several svara variants you are already familiar with (e.g. raga Harikambhoji, mela 28, resulting in Carnatic raga Mohana which resembles Hindustani raga Bhupali, also known as Bhup or Bhup Kalyan). For details on popular Hindustani ragas, refer to The Raga Guide by Joep Bor.
Once internalized you may want to contemplate and remember the same exercise with the help of the “8 x 8 beads” pattern shared here >>
Practice a different arrangement with 5 notes: raga Hamsadhvani >>
- This is the present version of raga Bhupalam, the earlier one would have corresponded to Revagupti, see below. [↩]
- According to P. Sambamoorthy this is the modern name for raga Bhupalam (commonly sung with notes derived from the 8th melakarta, Hanumatodi); also known as the Tamil pan Puranīrmai; in temples the earlier version of Bhupalam – the one based on 15th melakarta Mayamalavagaula – is rendered before dawn by nagasvaram players; and it used to be heard in women’s songs and other folk songs. – A Dictionary of South Indian Music and Musicians, Vol. I [↩]