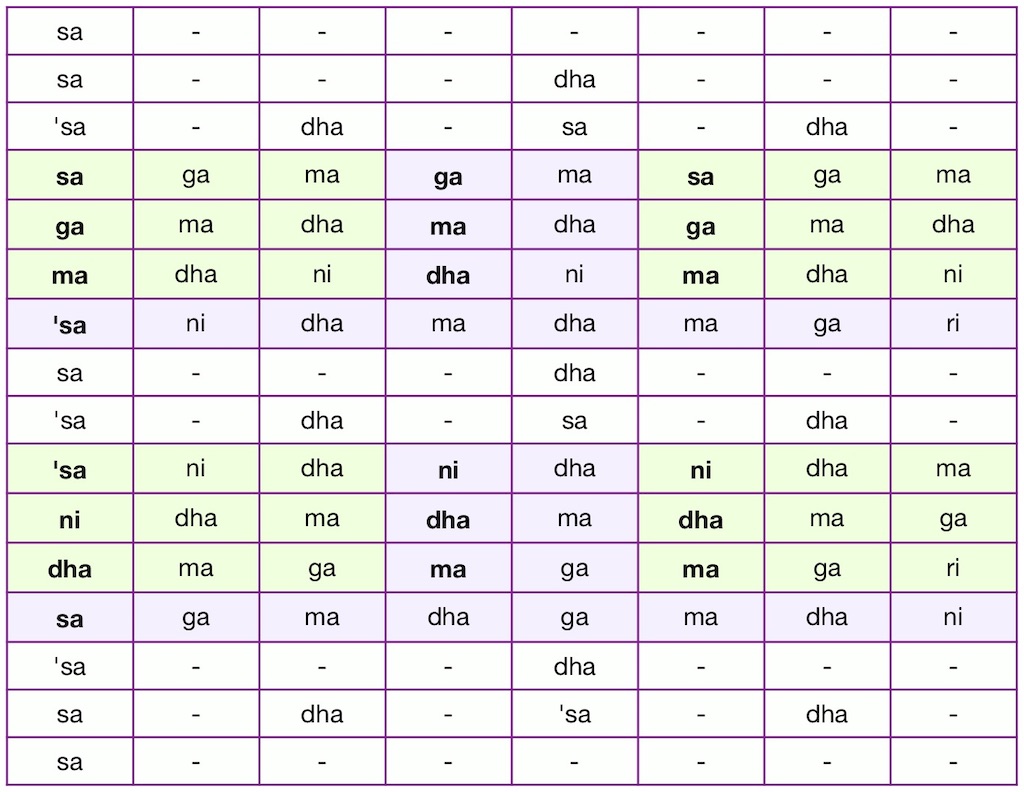
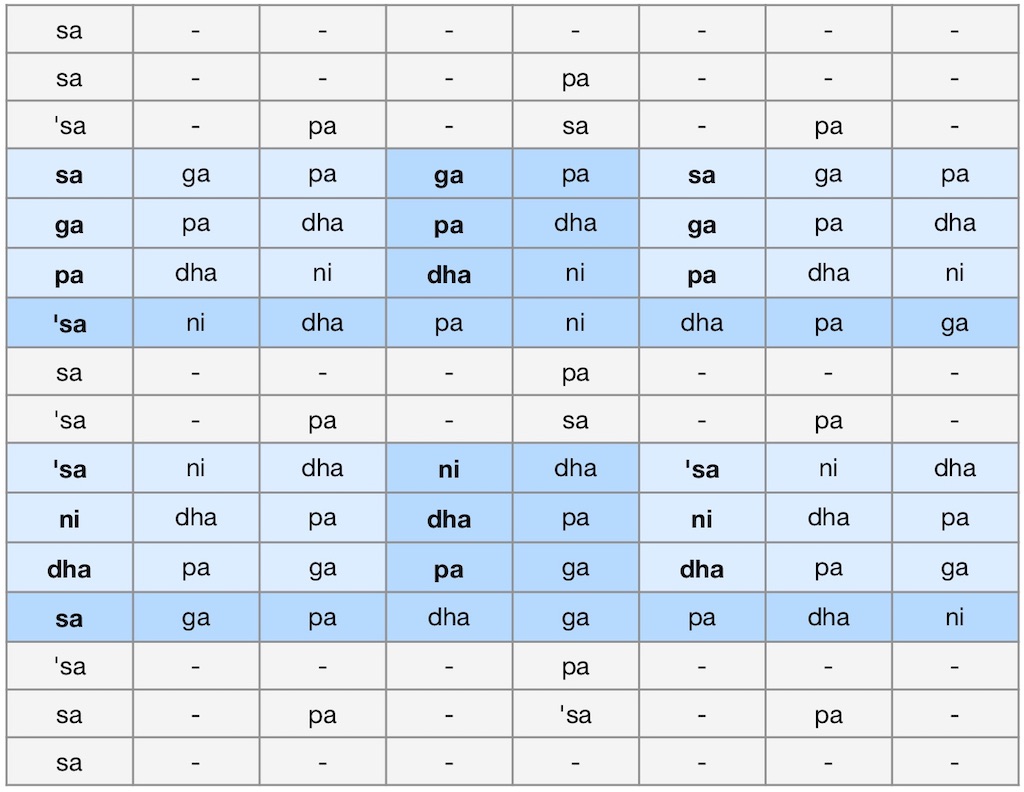
At first, this question seems easy to answer: just watch performers from either strand of Indian music and you’ll know Which is Which, merely going by the instruments in use, or how they dress and watching the body language involved: harmonium or sarangi vs. violin for melodic accompaniment for most vocal recitals, and tabla drums rather than a double-faced mridangam.

“Even at the peak of her career M.S.Subbulakshmi continued to
learn from other musicians” – R.K. Shriram Kumar >>
Tambura posture, fingering & therapeutic effect >>

Even in the absence of other clues, experienced listeners know what distinguishes one concert item from another, in order to immerse themselves in that which endows “classically trained” musicians across South Asia with a deeply felt sense of unity: raga, aptly defined as a “tonal framework for composition and improvisation” by Joep Bor in The Raga Guide.
What binds Hindustani and Carnatic music lovers together is the experience of raga which, given its roots (lit. colour, beauty, pleasure, passion), denotes a cultural phenomenon rather than just a particular combination of notes. This means that raga-based music is more widely shared than one would expect in the modern world due to its capacity to transcend linguistic boundaries. In short, both strands of Indian music, Hindustani and Carnatic music, have absorbed a wide range of regional traditions throughout history. At the same time, “raga music” continues to serve as a vehicle for meaningful lyrics in any conceivable genre in addition to “classical” or “devotional” music. Even when rendered by an instrumentalist or sung without lyrics (as customarily done within both Hindustani and Carnatic recitals) each raga constitutes “a dynamic musical entity with a unique form, embodying a unique musical idea”. […] As regards Hindustani ragas, they “are known to musicians primarily through traditional compositions in genres such as dhrupad, dhamar, kyal, tappa, tarana and thumri. Good compositions possess a grandeur that unmistakably unveil the distinctive features and beauty of the raga as the composer conceived it.” (Joep Bor).

the composers most revered and performed by Carnatic musicians
Muttusvami Dikshitar
Sri Tyagaraja
Syama Sastri
Painting by S. Rajam © Sruti Magazine >>
Composers on DhvaniOhio >>
A comparable range of genres is available to Carnatic musicians, including varnam, kirtana, kriti, ragam-tanam-pallavi, padam, javali, tillana with a notable difference: since the 16th century, Carnatic compositions take up more time in order to render the lyrics faithfully, as intended by their composers and jealously guarded by teachers, discerning listeners and critics alike.
It is hard to imagine how such ideas would have worked before the advent of the tambura or tanpura – another feature of Indian music which may explain why older scales and theories have fallen into oblivion ever since – in spite of frequent mentions in text books.
But it’s harder to explain the musical differences in plain language while listening attentively as their respective performances unfold: differences begin to multiply, mostly in ways too subtle for words. Such differences call for probing into the depths of Indian “classical” music in the sense of a particular branch of music that is governed by clearly defined rules as well as unwritten conventions valued by professionals and connoisseurs.
For Indian listeners, such distinctions are mostly associated with a particular region, like the northern Hindustani and southern Carnatic music even if deceptive when it comes to the birth places of noted Hindustani exponents: many famous musicians were born or trained in Bengal in the east, and Dharwad in the south, also known as “Hindustani music’s southern home“. Being associated with a famous regional tradition or lineage is mentioned in most programme notes, like the vocal gharana known as the “Dharwad Gharana” or “Gwalior Gharana” in Hindustani music; and likewise, southern musicians pride themselves for having learned their arts within a bani (“family tradition”) designated by a particular town, for instance Tanjavur (vocal), Lalgudi (violin) and Karaikudi (vina or veena).
Then there are the preferred languages used in song lyrics in the case of vocal music; and certain rhythmic patterns local listeners would instantly feel familiar with or, conversely, associate with “novelty” when first employed beyond their place of origin. The latter is eagerly anticipated toward the end of a recital. In the opening and main parts of a recital, the most obvious differences between Hindustani and Carnatic music include the following traits:
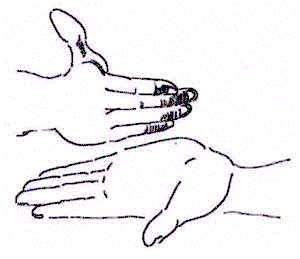
Art © Arun V.C.
- Hindustani musicians prefer “accelerating” almost imperceptibly – from slow to fast tempo – during an alap (raga alapana, the melodic improvisation preceding a composed theme); this preference entails presenting fewer items compared to their Carnatic peers;
- many (though not all) adhere to the convention of associating rāgas with a specific time of the day, or a particular season ;1
- by contrast, a typical Carnatic or Karnatak concert opens with two or three items in a brisk tempo, including sections in “double tempo”, before elaborating a particular raga in a slow-to-fast format akin to the Hindustani format known as “imagination” (khyal or khayal) traceable to 18th c. court music;
- Carnatic recitals are enriched by arithmetic elements derived from the repertoires of temple and dance musicians, and coordinated by visible gestures (something listeners love to emulate for the sake of self-immersion or as a sign of appreciation); and not surprisingly, rhythmic intricacies were successfully adopted and refined as part of Hindustani tihai patterns, most successfully by Ravi Shankar in the course of collaborations with southern instrumentalists (duly acknowledged in Raga Mala: The Autobiography of Ravi Shankar); be it for his solo sitar recitals or novel, mostly temporary jugalbandi ensembles like the one documented on video: recorded in 1974 at the Royal Albert Hall in London: “As far back as 1945, I was absorbing the essence of these from the fixed calculative systems of the Carnatic system.” (To understand their application, watch a tarana on YouTube repeatedly, starting from 3:27) Unsurprisingly this process of give-and-take, once proven successful, has become too common to bother crediting it to any particular source, other than declaring it a “shared heritage” cherished by musicians and audiences all over the world: Unity in Diversity at its very best!
To appreciate some of the aforementioned characteristics in the context of South Indian music, listen to recitals by two of its most beloved exponents:
From the above mentioned differences follows the most important one, namely the amount of time assigned to compositions based on elaborate lyrics: the concise bandish in a Hindustani recital vs. the tripartite kriti several of which occupy pride of place in Carnatic music.
The standard syllabus for South Indian “classical” music is ascribed to 16th c. composer Purandara Dasa of Vijayanagar (modern Hampi in northern Karnataka as indicated on the music map seen below). His method proved so efficient as to provide a common ground for aspiring singers or instrumentalists from many regions and linguistic backgrounds. This may explain how such music invites the convergence of several voices or instruments into one (unison): a soloist accompanied by violin just as two vocalists (popular duos known as “Brothers” and “Sisters”), or pairs of flutes, lutes (vina) and violinists, all capable of achieving perfect alignment at any given moment during a recital; and this not merely for evenly paced motifs but with equal ease in richly embellished passages. For good measure, such feats require neither notation nor lengthy rehearsals but instead combine musical memory with considerable freedom to enrich predictable patterns with one’s own flights of imagination.
As regards inevitable specialization such as a particular vocal or instrumental style, required for mastering certain melodic and rhythmic intricacies and compositions, there is an infinite variety to delve into: variety that explains the evolution of two great music “systems” that kept evolving and intersecting ever since musicologists became obsessed with classifying and validating certain features in the 19th and 20th centuries.
For non-Indian music lovers and students, Yehudi Menuhin’s reminiscences titled “Unfinished Journey” may be a good starting point: the violin virtuoso was among the first to appreciate fact that “Indian musicians are sensitive to the smallest microtonal deviations, subdivisions of tones which the violin can find but which are outside the crude simplifications of the piano (or harmonium)”. His interest in Indian violin music motivated Menuhin to invite the South Indian violin virtuoso Lalgudi Jayaraman to tour the UK and participate in the 1965 Edinburgh music festival.
For a better understanding of what Yehudi Menuhin meant by “smallest microtonal deviations”, listen to the very first composition most learners of Carnatic music have learned – a gitam (didactic song) by Purandara Dasa – in: A brief introduction to Carnatic music >>

“The classical music of the West has influenced
our musical culture” – Manohar Parnerkar in
Sruti Magazine August 2019 >>
Since then, musicians from various backgrounds have never ceased to contribute to an unprecedented intercultural dialogue: exponents of western classical, ecclesiastical and minimal music just as jazz, pop and film music, all set to explore new horizons together with their Indian peers.
Tips
- to explore the above topics on your own, refer the Indian sources recommended here >>
- in order to get a clear idea what this means in practice, listen closely to audio and video contents featuring two prominent families of violinists whose roots lie in South India: one known as the Parur bani (brothers M.S. Gopalakrishnan & M.S. Anantharaman), and the other brought into prominence by N. Rajam (Hindustani violin) and her brother T.N. Krishnan (Carnatic violin)
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Michael Zarky (Tuning Meister) for providing valuable tips and corrections for this post and previous Carnaticstudent courses including those offered in conjunction with university eLearning programmes.
More about the above person(s) and topics
Periodicals and sites included | More resources | Disclaimer >>

Photo © Ludwig Pesch
Learn & practice more
- A brief introduction to Carnatic music (with music examples and interactive map)
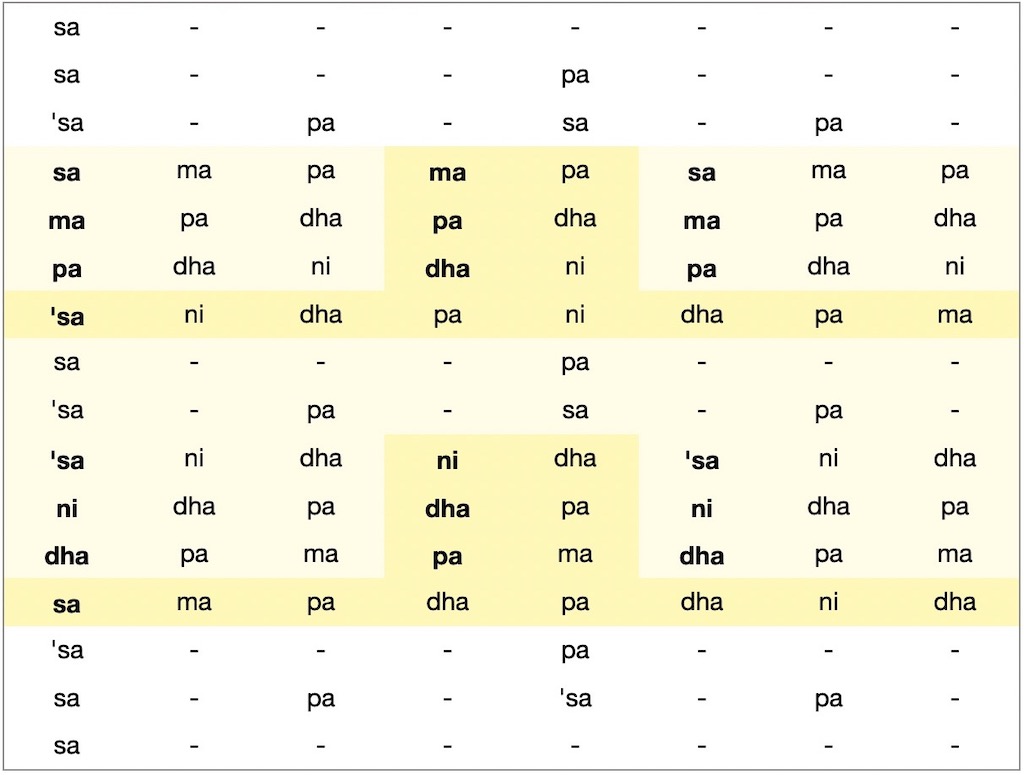
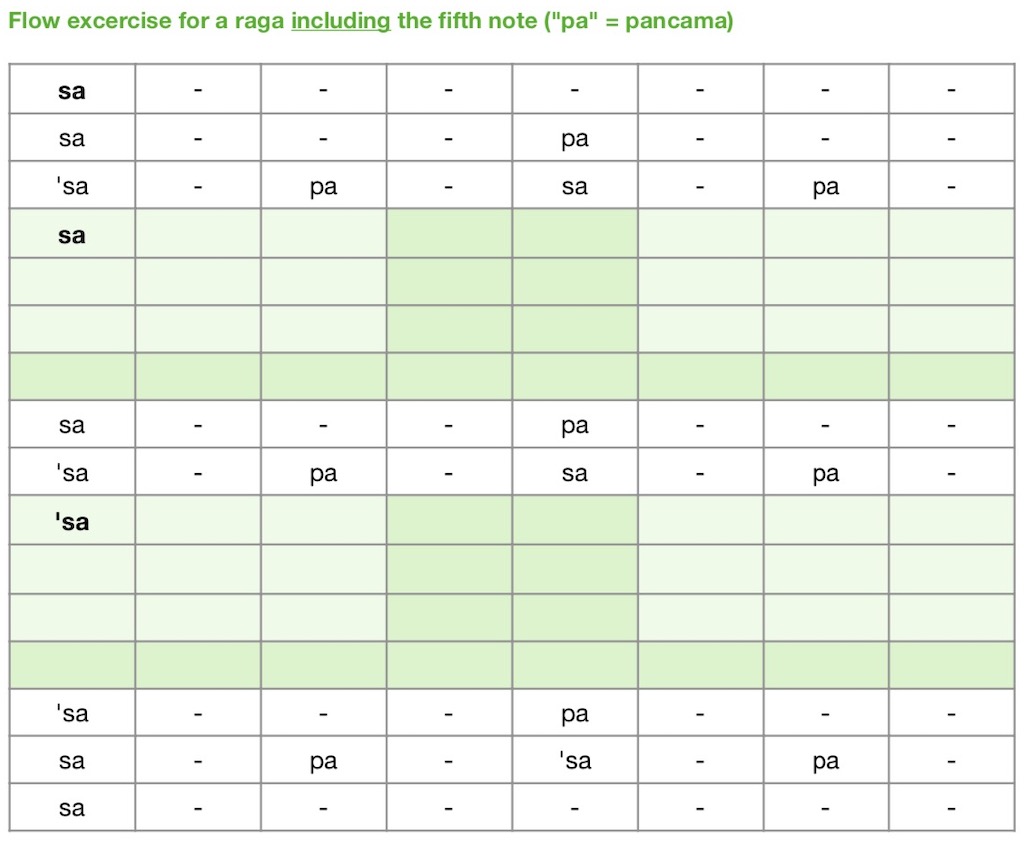
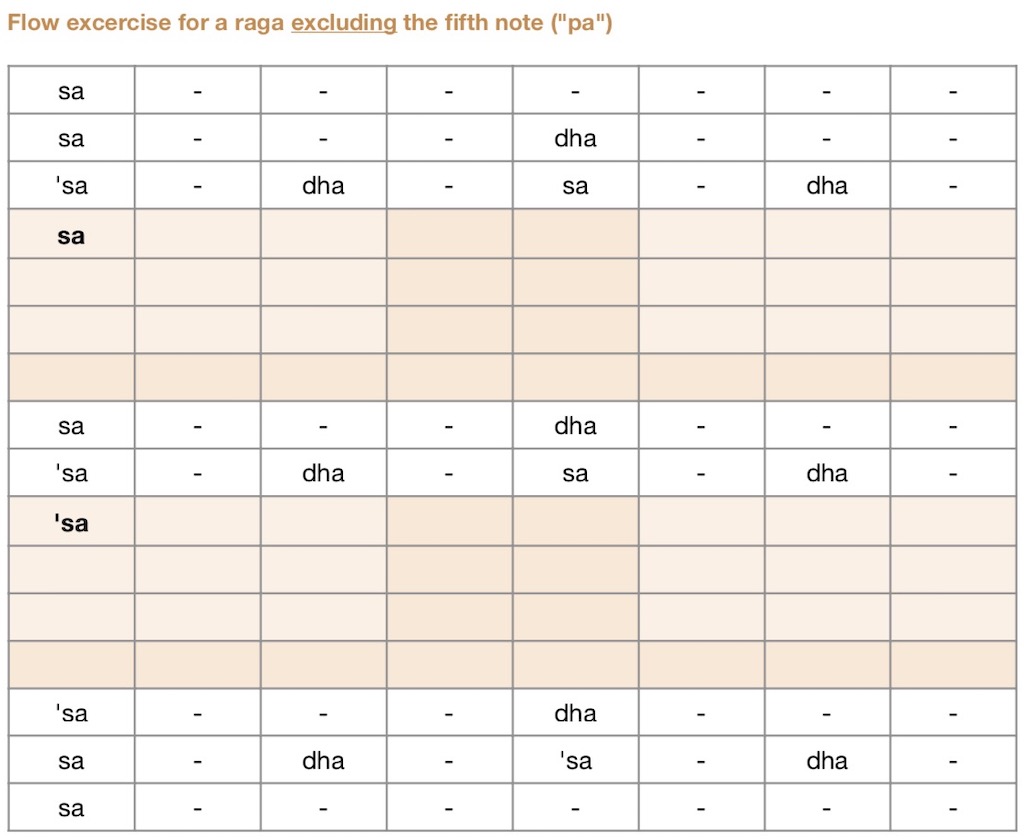
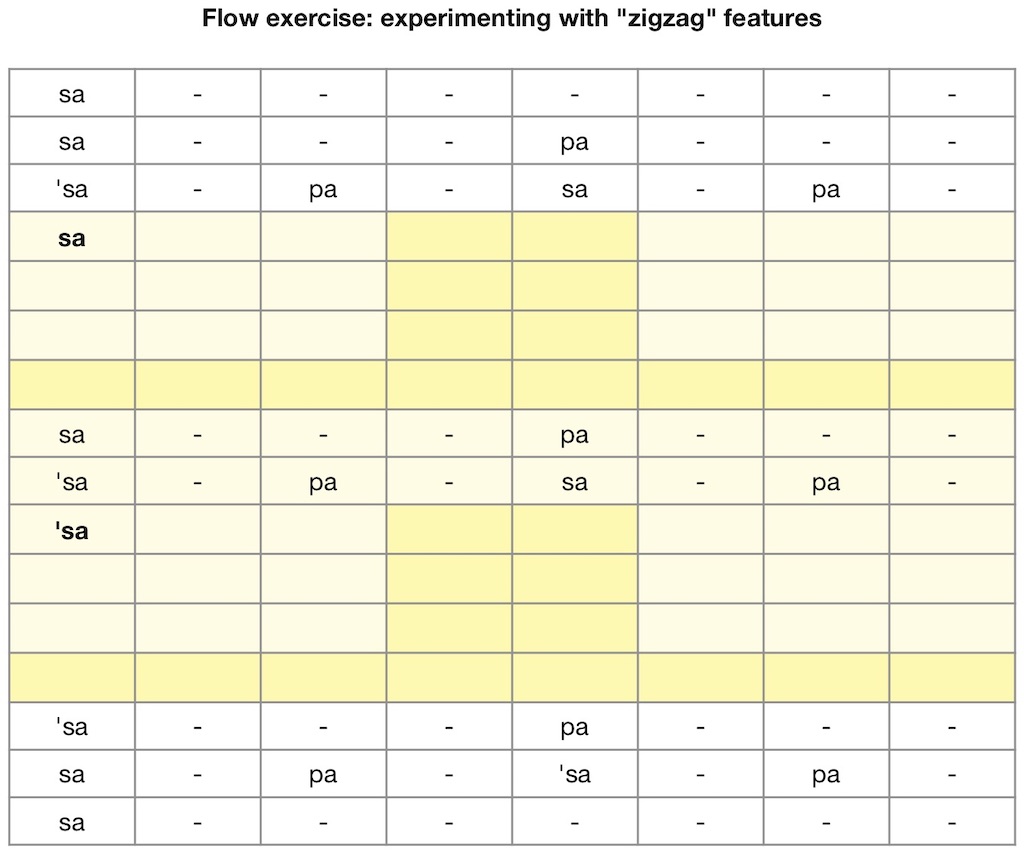
- Free “flow” exercises on this website
- Glossary (PDF)
- Introduction (values in the light of modernity)
- Video | Keeping tala with hand gestures: Adi (8 beats) & Misra chapu (7 beats)
- Voice culture and singing
- Why Carnatic Music Matters More Than Ever
- Worldcat.org book and journal search (including Open Access)
- Noted musicologist V. Premalatha comes to the conclusion that as an “extra-musical factor”, association of time with rāga “survives very strongly in the North Indian system of music and has not affected the South Indian Music“. [↩]